Heat Treatment of Die Castings-4
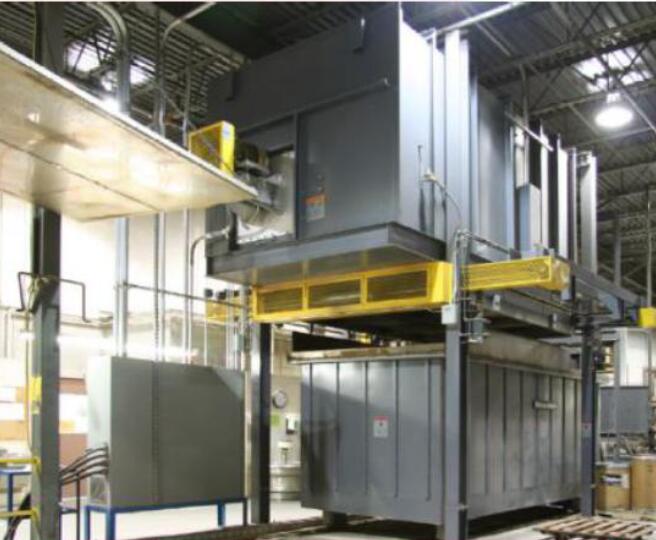

1.Heat Treatment Specification
To avoid over-burning, increase the heating temperature as much as possible to promote a more strengthening phase to dissolve into the matrix. The holding time can be selected according to the chemical composition of the alloy, the casting method, the wall thickness of the casting, and other factors.
The quenching cooling medium of cast aluminum is generally hot water to reduce the deformation of the casting.
If the casting is deformed after quenching, it can be corrected in the quenched state. When correcting, the force should not be too strong, but it should be slow and even. Castings that need to be artificially aged should be aged as soon as possible after quenching. If the limitation period is interrupted for any reason, the limitation period can be accumulated.
After heat treatment, if the mechanical properties are unqualified, repeated quenching can be carried out. The heating time of repeated quenching can be appropriately shortened, and the number of repeated quenching shall not exceed two times.
In order to ensure the quality of heat treatment, necessary inspections and corresponding records should be made for its main processes.
2.Heat Treatment Defects and Preventive Measures
Crack
Defect performance:
- Small cracks
- Twists and turns not straight
- Dark grey
- Cracked
Possible reasons for exception:
- Quenching water temperature is too low
- The heating rate of the solid solution is too fast, and the furnace temperature is uneven
- Improper water direction of the workpiece during quenching
Countermeasures:
- Increase the quenching water temperature and replace the quenching medium if necessary
- Slow down the heating rate and adopt an isothermal solid solution process
- Choose the correct launching direction
Deformation Warping
Defect manifestation:
- Dimensional change
- Shape change
Possible reasons for exception:
- Quenching water temperature is too low
- The solution heating rate is too fast
- Improper water direction of the workpiece during quenching
- Improper charging method
- Unreasonable casting structure design
Countermeasures:
- Increase the quenching water temperature and replace the quenching medium if necessary
- Slow down the heating rate
- Choose the correct launching direction
- Using special anti-deformation fixtures, those with small deformation can be corrected in time after quenching
Overheated
Defect performance:
- Nodules on the surface,
- Decreased elongation
Possible reasons for exception:
- The local temperature in the furnace exceeds the alloy overfire temperature
- Heats up too fast
- Failure of measuring and controlling temperature instruments
- Excessive content of low melting point elements
Countermeasures:
- Heat up at a rate not exceeding 3°C/min
- Regular inspection and calibration of measurement and control instruments
- Strictly control the content of low melting point alloying elements
Uneven quenching
Defect performance:
- High hardness in thin-walled parts
- Low elongation
- Hardness in thick parts (especially the inner center)
Possible causes of abnormality:
- Heating
- Uneven cooling
Countermeasures
- Re-heat treatment, reduce the heating rate and prolong the holding time
- Try to cool all parts of the casting at the same time
Mechanical properties are unqualified
Defect performance
- Unqualified strength and elongation
Possible reasons for exception:
- Low solution temperature
- Insufficient holding time
- Quenching water temperature is too high
- Deviations in alloy chemical composition
Countermeasures:
- Re-annealing
- Increasing the solution temperature
- Prolonging the holding time
- Decrease the quenching water temperature
- Adjust the repeated heat treatment parameters according to the specific deviation elements and deviations
Surface corrosion
Defect performance:
- Spots or lumps on the surface (different color from other parts)
Possible reasons for exception:
- High humidity inside the furnace
- It contains other harmful substances such as sulfides
Countermeasures:
- Drying of baskets before furnace loading
- No residues such as lubricants on the workpiece surface
3.Determination of Heat Treatment System for Aluminum Alloy Die Castings
The core elements of the heat treatment system:
- Solution temperature
- Solution time
- Quenching speed
- Aging temperature
- Aging time
The basis for determining the heat treatment system:
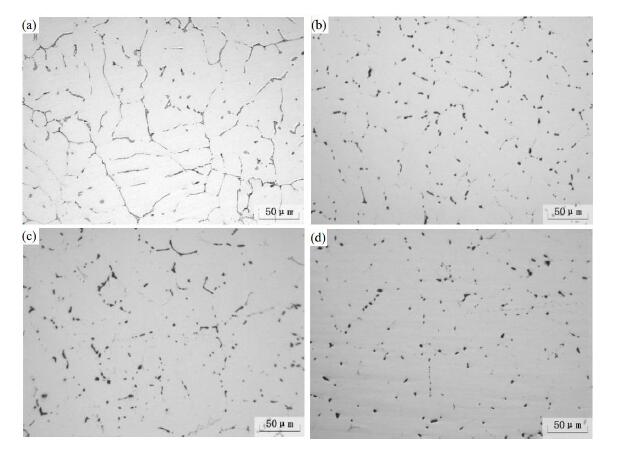
- Microstructure
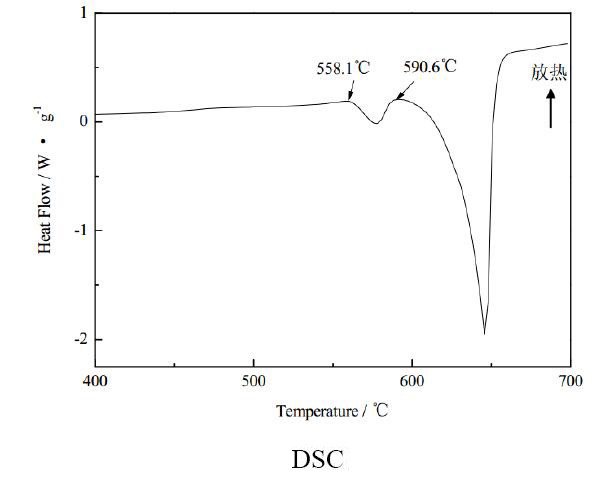
- DSC/DTA test curve
- Brochures/Information
- Theoretical calculations
- Orthogonal experiment
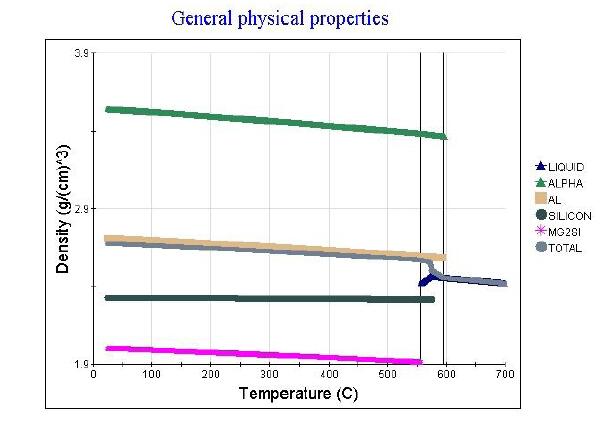
Solution treatment temperature selection T=0.9~0.95T( melting)
The holding time t usually depends on the alloy composition, structure, and solution temperature, which can be obtained from the following formula:
t=(t0+t1E)·H+ tc
In the formula,
H is the maximum thickness of the phase,
t0 is the heat penetration rate,
t1 is the nominal solution time,
tc is the basic holding time,
E is the correlation enhancement coefficient.
The E value is proportional to the ingot smelting quality coefficient, alloying coefficient, mechanical property direction coefficient, variety coefficient, grain size coefficient, state coefficient, aging category coefficient, and inversely proportional to the deformation coefficient and deformation compensation coefficient.
4.Heat Treatment Equipment
Main technical requirements of heat treatment equipment
- Since the temperature difference between quenching and aging of aluminum alloy is not large (because the quenching temperature is close to the melting point of the low-melting eutectic component in the alloy), the temperature difference in the furnace should be controlled within ±5 °C.
- The temperature measurement and temperature control instruments are required to be sensitive and accurate to ensure that the temperature is within the above error range.
- The temperature of each zone in the furnace should be uniform, and the difference should be within the range of 1-2 °C.
- The quenching tank has a heating device and circulation device to ensure the uniform heating and temperature of the water.
- The polluted cooling water should be checked and replaced regularly.
Heat Treatment Quenching Medium
Quenching medium is an important factor in ensuring the realization of various heat treatment purposes or functions. The higher the cooling rate of the quenching medium, the more intense (fast) the cooling of the casting, the higher the degree of supersaturation of the α solid solution in the metal structure, and the better the mechanical properties of the casting, because a large number of strengthening phases such as intermetallic compounds are solid-dissolved into the α solid solution of Al.
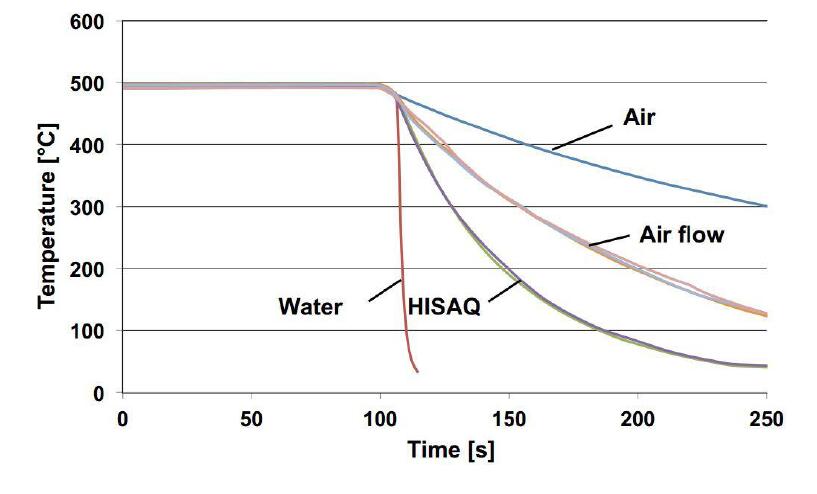
The quenching medium according to its cooling speed to the casting is a mixture of dry ice and acetone (-68°C), ice water, room temperature water, 80-90°C water, 100°C water, atomized water, various oils (rapeseed oil, etc.), various oils heated to 200-220 ℃, air, etc.
Considering the deformation, the air is suitable for the quenching medium of aluminum alloy structural parts.
Heat Treatment Furnace Configuration
- Solid melting furnace
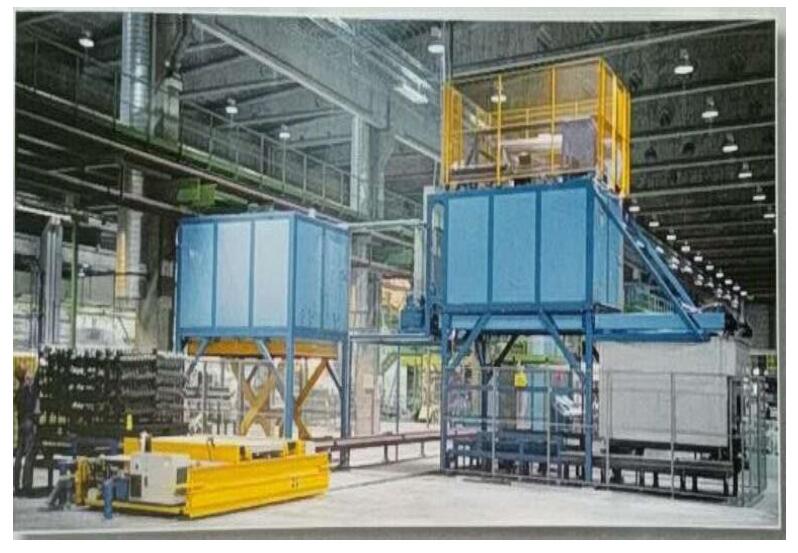

- Quenching tank
- Aging furnace
- Cooling section
- Loading and unloading parts
- Sand removal device
- Storage, holder
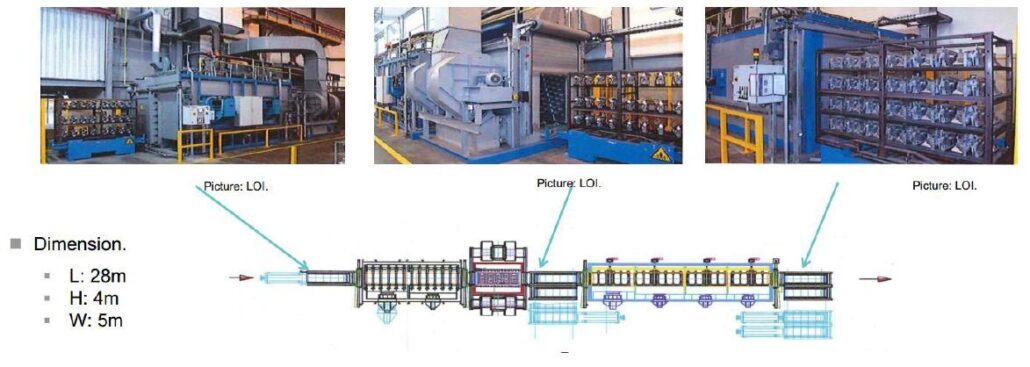
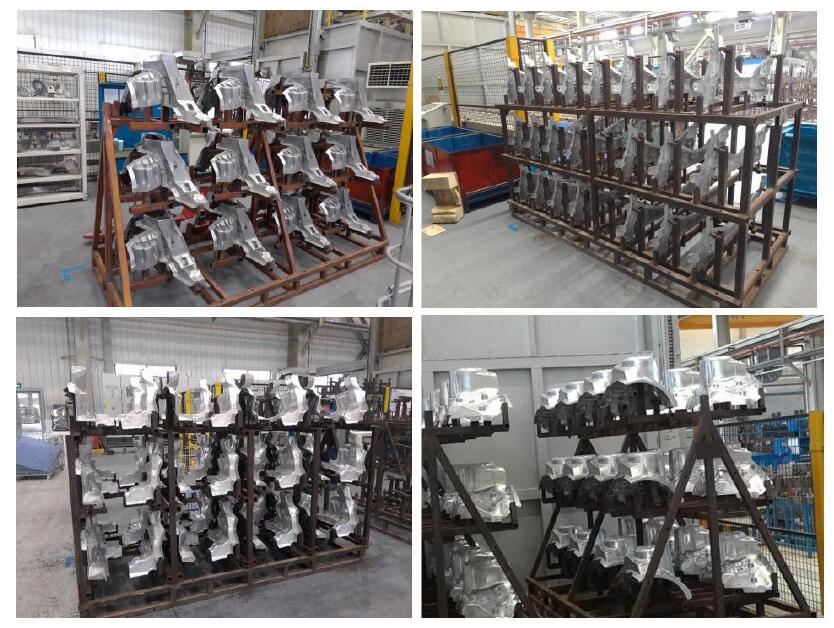
Storage Racks and Holders
Casting storage is also a very important heat treatment knowledge. Therefore, pay close attention to the following issues:
- In order to be able to provide a uniform rapid cooling effect for all castings, it is important to have good continuous air circulation.
- Air quenching is carried out under the condition of wind speed of 120km/h; in order to avoid the deformation of the casting, it is very necessary to fix the bracket for the casting.
- In order to achieve a more economical heat treatment, an optimized loading density is also crucial.


5.Heat treatment process (take a die casting T6 as an example)
Device overview:
This equipment consists of a solid melting furnace, quenching device, aging furnace, conveying device, and sand removal device.
Objects to be processed:
The size of the object to be processed in 267 widths × 114 height × 410 lengths (MAX)
Weight 10~13kg/1pce (including neutron sand weight 0.75kg)
Material basket:
Size: 1320 L×1320 W×650 H
Hourly processing capacity: 64/55*60=68.8 pieces/hour
Annual production: 68.8*24 hours*26 days/month*December=515, 174 pieces/year
90% open rate: 515,174*90%=463,656 pieces/year
Processing conditions:
1.Solid melting furnace
Processing turnaround time:
basket/55 minutes,
heating 80 minutes,
soaking 360 minutes/500±5℃ (temperature of workpiece to be processed),
water temperature 60~90±5℃ (quenching),
within +10℃ after quenching (quenching time) 5 minutes),
and complete the action from opening the door of the solid melting furnace to entering the water in the material basket within 26 seconds.
2. Aging furnace
Processing turnaround time:
baskets/50 minutes,
heating for 60 minutes,
soaking for 240 minutes,
215±5℃ (temperature of workpiece to be processed),
forced cooling to below 50℃ within 60min.
3. Heating fuel:
LNG (natural gas), gas supply pressure 10KPa, calorific value 8500~9500Kcal/Nm3.
4. Heating method: hot air circulation method
5. Transmission method: driven by drum motor, with frequency conversion control device
6. Furnace door opening and closing method: motor lifting method and cylinder top pressing method
7. Noise control standard: 85dB(A), test at a distance of 1 meter around the furnace body and a height of 1 meter above the ground.
