How to Prevent Die Casting from Corrosion?
When you invest a huge amount of money, you purchase a batch of die-casting parts and store them in a warehouse.
Sometimes after a few days of continuous rain and a relatively high temperature of about 30 degrees(86F), rust start growing on your die casting parts.
If you recheck the product, you will find many white and black spots on the casting surface. In many cases, the casting itself has no defects, and just because of mold, you tend to scrap this batch of products.
As a result, you experience significant economic loss! Hence the corrosion of die castings.
Many other names for this phenomenon include rust, blackening, yellowing, mildew, and spots. However, we collectively call it corrosion.
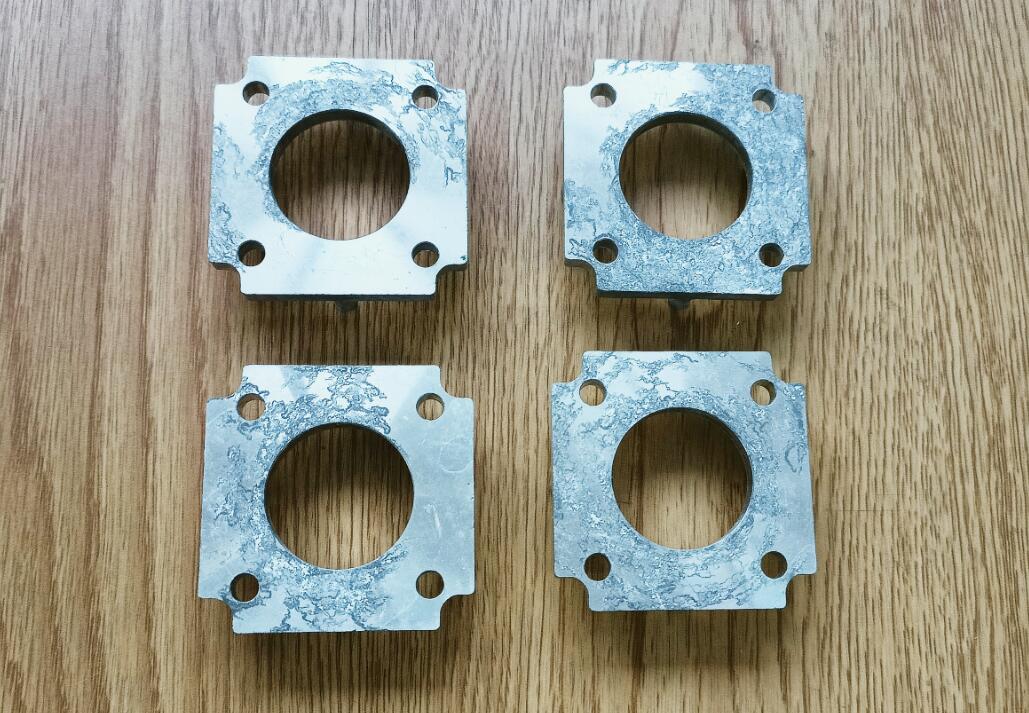

1.What Causes Corrosion on Die-Casting Parts?
Corrosion on die-casting parts continue to be a major problem; hence we should identify its causes. Of course, there are two main reasons, and we outline them below.
- Corrosion of aluminum alloy
- Mildew of aluminum alloy
Aluminum is an active metal that easily reacts with water in the air, loses electrons, and turns into aluminum ions. Therefore, aluminum is easy to oxidize and turn black, determined by its characteristics.
2. What is the Corrosion of Aluminum Alloy?
The corrosion of aluminum alloy refers to the electrochemical action occurring in the environment, which causes the composition of the aluminum alloy to change. The change in the composition of the aluminum alloy reduces its performance. Aluminum, magnesium, and zinc are all active metals and react very easily to corrosion.
The corrosion of aluminum alloy falls into two categories:
- Chemical corrosion
- Electrochemical corrosion
Chemical corrosion of aluminum alloy
In this concept, the aluminum alloy is in contact with the gas or liquid in the environment, and the oxidation-reduction reaction occurs directly. Aluminum loses electrons, turns into aluminum cations, and undergoes an oxidation reaction. As a result, it changes the aluminum alloy’s appearance, color, and mechanical properties.
Note: As the temperature increases, the rate of chemical corrosion will significantly increase.
Electrochemical corrosion
Electrochemical corrosion means that the impure aluminum alloy is in contact with the electrolyte solution, and the galvanic reaction occurs. In an acid solution, aluminum loses electrons and is oxidized, while hydrogen ions gain electrons and become hydrogen gas. So it is also called hydrogen evolution corrosion.
In a weakly acidic or neutral solution, aluminum loses electrons, oxygen gains electrons, and aluminum becomes alumina. So it is also called oxygen corrosion. Therefore, the main component of aluminum rust is alumina.
Note: The corrosion of aluminum alloys is mainly electrochemical.
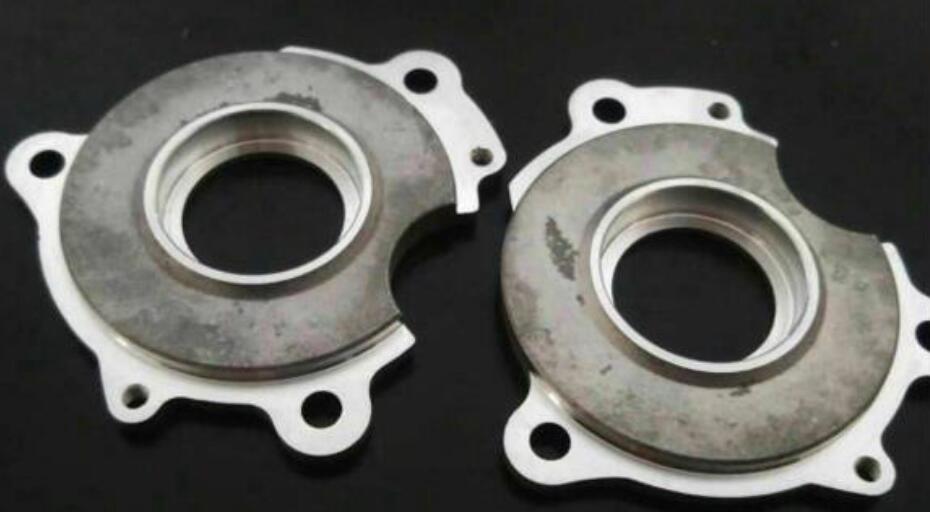

3. What is the Mildew of Aluminum Alloy?
Microorganisms cause mildew. Under suitable temperatures (10-40 degrees, 25-40 degrees most active) and humidity (greater than 65%), microorganisms multiply and grow on the aluminum alloy surface, producing local white patches.
The following are the leading causes of mildew:
- The storage environment, temperature, and humidity of die castings are very suitable for the growth of mold
- The surface of the die-casting product mixes with substances that can easily absorb moisture, forming a galvanic corrosion reaction on the surface of the die-casting product. Hence creating an environment suitable for mold growth
- Uncleaned grease on the surface of the die casting. When the temperature and humidity are appropriate, the mold will grow rapidly
4. How to Prevent and Control Aluminum Alloy Corrosion?
From the analysis of the causes of moldy die-cast aluminum, the problem of mildew and oxidation is due to several factors. The factors include alloy properties, process flow, surface treatment, storage, and other aspects.
At the same time, when carrying out all processes such as cleaning, inspection, storage, and transportation, you need to consider mildew and oxidation, which will cause corrosion. Therefore, this is a comprehensive problem that needs consideration from the overall process of die-casting production.
4.1 Aluminum Alloy Materials
The content of copper in the aluminum alloy determines the corrosion resistance of the aluminum alloy. The higher the copper content, the worse the corrosion resistance, and the easier it is to produce intergranular corrosion. So it’s best to use materials with lower copper content.

4.2 Aluminum as a Lively Metal
Since aluminum is a lively metal, you can use surface passivation to transform the surface of metal castings into a state that is not easy to be oxidized. The action will effectively delay the corrosion rate of die castings.
4.3 Choice of Release Agent
Mold release agents play a vital role during the die casting production process. Therefore, it would be best to choose a neutral or alkaline mold release agent when choosing mold release agent. The acid mold release agent is very corrosive to die castings.
Do not use mold release agents containing plant fibers. Instead, it is best to use good quality and brand-name release, agents. Moreover, checking the mold release agent proportioning machine should be done regularly. If the mold release agent is deteriorated or even smelly, it needs to be cleaned in time and replaced with a new release agent.
4.4 Effect of Cutting Fluid
The cutting fluid is a crucial element that features in the die casting process. Therefore, it is best to use an oil-based anti-rust cutting fluid instead of fluids containing plant fiber.
4.5 Use of Cleaning Agent
There are cleaning agents that support corrosivity. Therefore, you should not use cleaning agents that boost corrosive activity. For example, it is not proper to use acidic cleaning agents, but neutral cleaning agents are the best fit.
4.6 Cleaning and Drying of Die Castings
After machining the die casting, you should clean it quickly and thoroughly. After machining, rinse with water, and it is impossible to clean the residual release agent and cutting fluid on the surface of the die casting.
It is best to use ultrasonic cleaning to wash away the release agent and the cutting fluid on the surface. And after cleaning, it is best to dry the product. If there is no drying condition, the most basic measure is to use an air gun to dry the surface moisture.
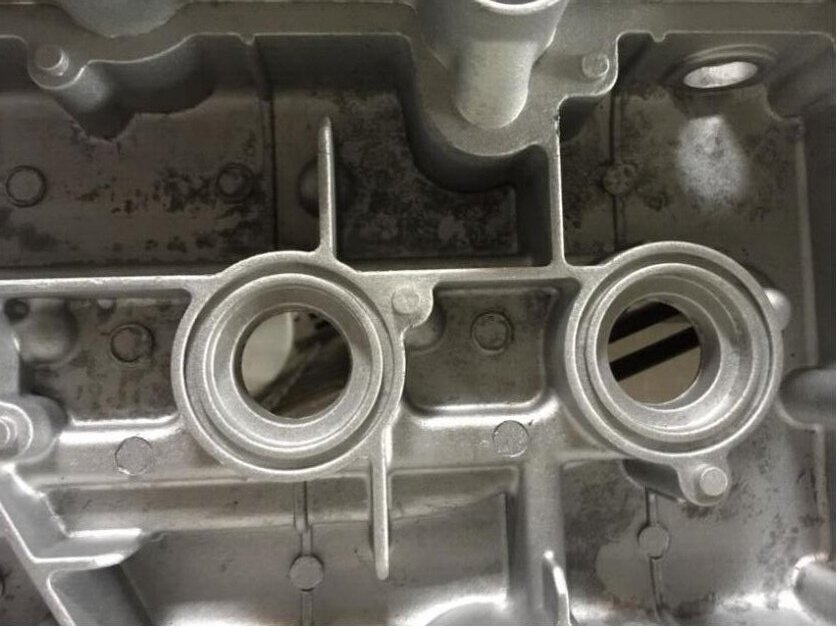
4.7 The Packaging of Die Castings
The carton used for packaging is very susceptible to moisture. Moreover, the carton is alkaline. Therefore, if you store the die-casting for a long time, the surface of the die-casting part should not be in direct contact with the carton; otherwise, the contact position will be black and moldy.
You can use bubble paper or pearl cotton to separate the die casting from the carton. You should wrap unused cartons with stretch film to prevent moisture. If the requirements of die-casting products are relatively high, they can be packaged in plastic bags separately while placing desiccant in the bag.
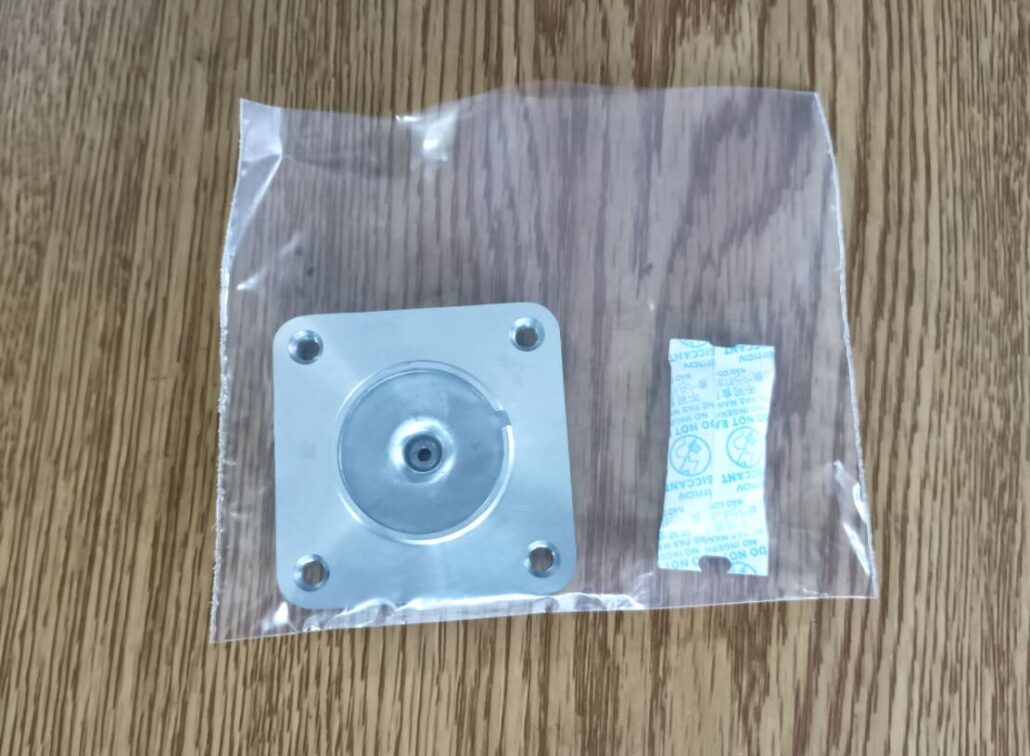

4.8 About Storage
Die-casting parts should not be stored in the open air for a long time, resulting in the accumulation of dust on the product’s surface. A stretch film will be beneficial when packing the product packaging box on the pallet.
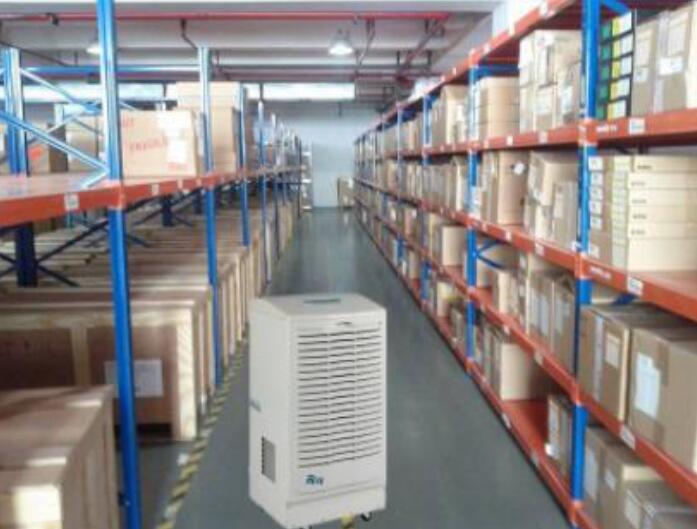
Warehouses are the usual storage points for die-casting parts, and the shelf should be as high as possible from the ground, and the warehouse should be kept dry and ventilated. In rainy seasons(particularly humid), you can use a dehumidifier to keep the warehouse dry. All materials in contact with die castings need to be kept dry.

4.9 Regarding Transportation
If long-term shipping is required, sometimes the container is not completely sealed. As a result, water vapor and salt in the sea can easily cause moldy die castings. Instead, you can put a desiccant in the container to absorb moisture.
5. How to deal with corroded die castings?
Let’s get familiar with a few facts below;
Generally for aluminum alloys,
- If the die-casting is corrosion and black, the materials in contact are generally alkaline
- If the die-cast part is corrosion and white, the material in contact is generally acidic
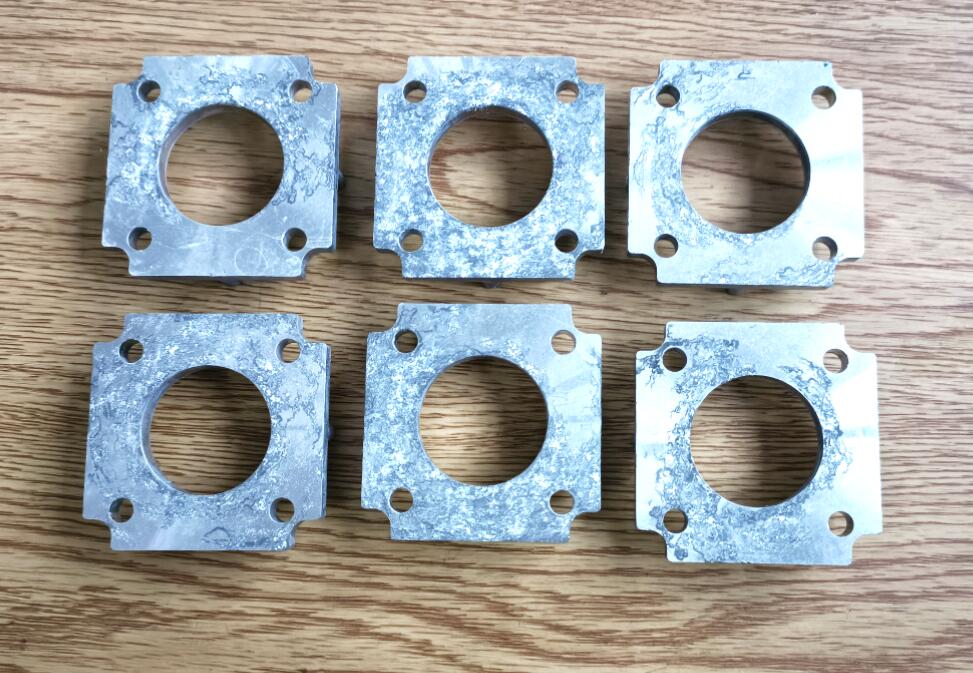

Once you identify moldy die castings, it is best to take quick countermeasures. If left alone, the corrosion increases and reprocessing may be useless. In addition, you cannot clean rust spots on die-casting parts with ordinary kerosene, cleaning agents, and degreasing powder.
Corroded die castings are difficult to clean, and there is no guarantee that they are completely clean. However, you can only try the following methods for processing.
- Sandblasting or shot blasting (oxidation and mildew are relatively light).
- Ultrasonic cleaning (lighter oxidation and mildew);
- Magnetic grinding (oxidation and mildew are heavier)
- Pickling (oxidation and mildew are heavier)
Pickling requires attention to concentration, temperature, time, etc., and involves environmental protection and sewage discharge issues. Therefore, it is best to hand it over to a professional surface treatment manufacturer. After treatment, passivation treatment should be the next step.
